When it comes to character animation, hand posing can make or break the believability of the overall performance. In this clip from an AnimSchool Facial Performance class, instructor Thom Roberts demonstrates some tips for posing hands with more appeal.
Starting with a Natural Pose
The default hand is typically flat and rigid, with no natural form to it. Instead, consider forming a more neutral and relaxed pose. In this state, fingers naturally arc across the palm rather than lying straight. Rotating the fingers slightly in the Y-axis introduces this natural curvature and immediately makes the hand feel more lifelike.
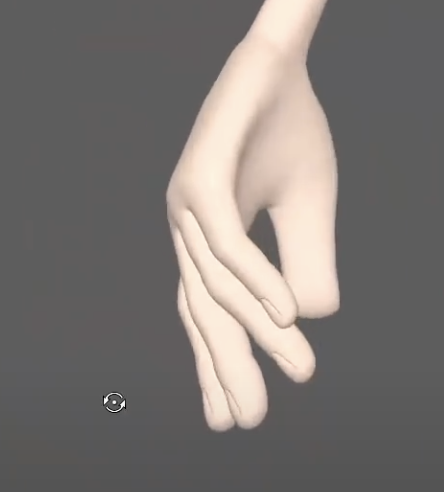
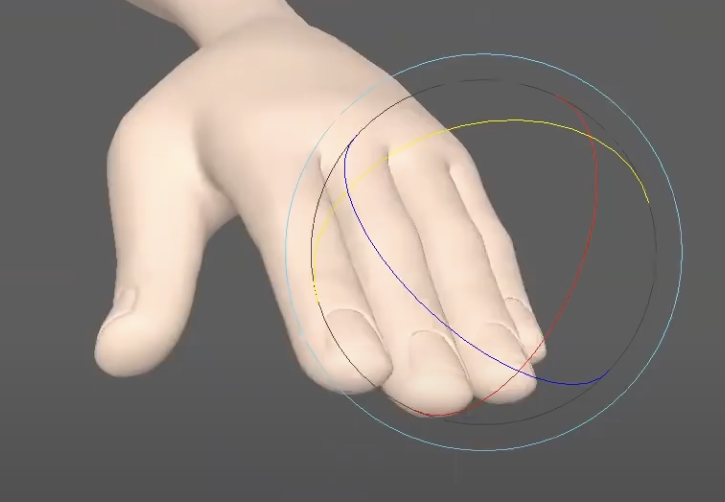

Notice how the left pose feels stiff, while the right feels relaxed.
Breaking the symmetry is also an important step in creating a natural feel. By default, fingers are perfectly aligned and parallel. Introducing subtle rotation helps avoid that uniformity. For example, as soon as you rotate the fingers in Y, it allows for natural overlaps when rotating in X. This technique helps simulate how fingers rest and move in real life — with the pinky slightly overlapping the ring finger, and so on. A common mistake in hand posing is overusing the third finger joint (the one closest to the fingertip). In a relaxed hand, most of the curvature comes from the first and second joints. The final joint is usually reserved for poses that require tension, like clenching or grasping.
When transitioning into more specific poses like a fist, the trick is to maintain visual interest and avoid robotic symmetry. For instance, keeping the index finger slightly elevated or angled differently can add personality and interest to the pose. Avoid even spacing between knuckles — subtle variations help sell the realism.
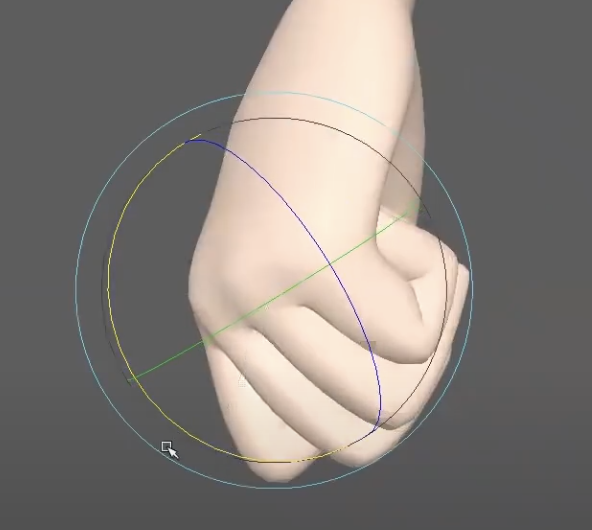
In quick animation or stylized movement, you can exaggerate hand poses to emphasize motion. This might include scaling fingers or grouping them for a simplified, dynamic silhouette. The goal is to support the direction of the movement and reduce distracting negative space between fingers.
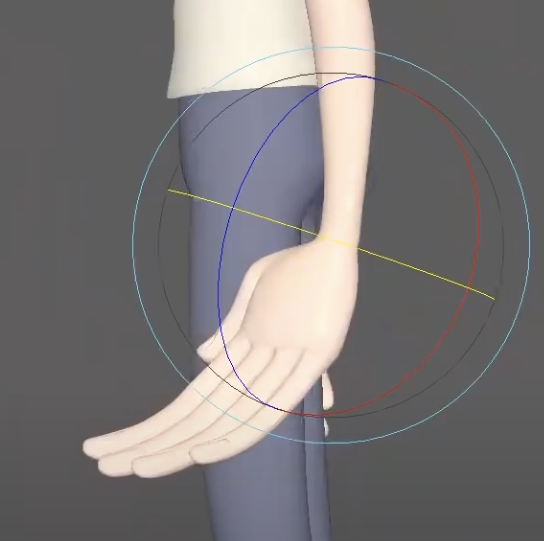
Crafting great hand poses in Maya takes more than just rotating joints; it requires an understanding of anatomy, asymmetry, and the visual language of movement. Focusing on these small but meaningful adjustments will elevate the overall animation and bring the characters to life.
Watch the full clip from an AnimSchool lecture here:
At AnimSchool, we teach students who want to make 3D characters move and act. Our instructors are professionals at film and game animation studios like Dreamworks, Pixar, Sony Pictures, Blizzard & Disney. Get LIVE feedback on your Animation from the pros. Learn more at https://animschool.edu/