When animating any sort of physical action, understanding and being able to effectively convey force is crucial. It’s about using motion to communicate struggle, weight, and intention. In this clip from a live AnimSchool lecture, instructor Anthea Kerou discusses the basic principles of animating weight. Through the classic “lift a heavy object” animation assignment, Anthea demonstrates what key features your animation should have in order to create a feeling of believable weight and force.
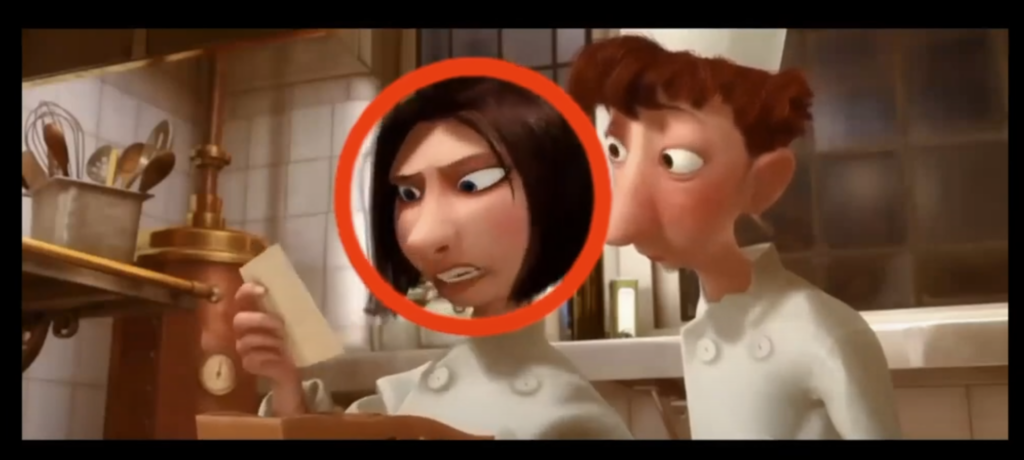
Force and weight becomes visible through the pose. A character pushing a heavy object won’t stand straight—they’ll lean, brace, and shift their center of gravity. This imbalance, with feet pushing backward and the torso leaning forward, is how animators signal effort. If a character’s center of gravity stays balanced, it won’t convincingly show that the object is heavy. Another useful way to assess how heavy an object is is the relationship between effort and effect. If a character puts in little effort but causes a big movement, the object appears light. But if there’s a lot of effort and little effect—like a character straining to lift something that barely moves—it signals weight and struggle, and force being applied.
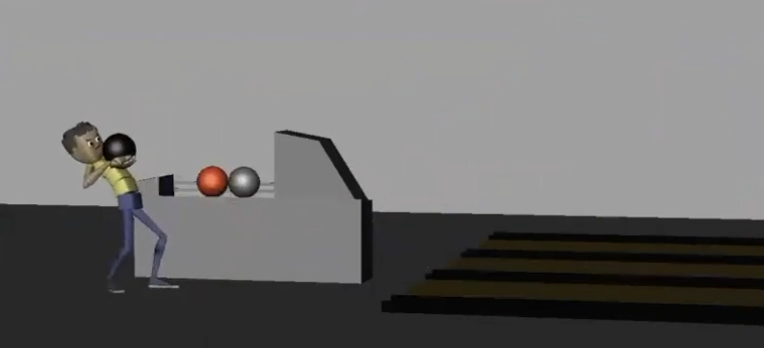
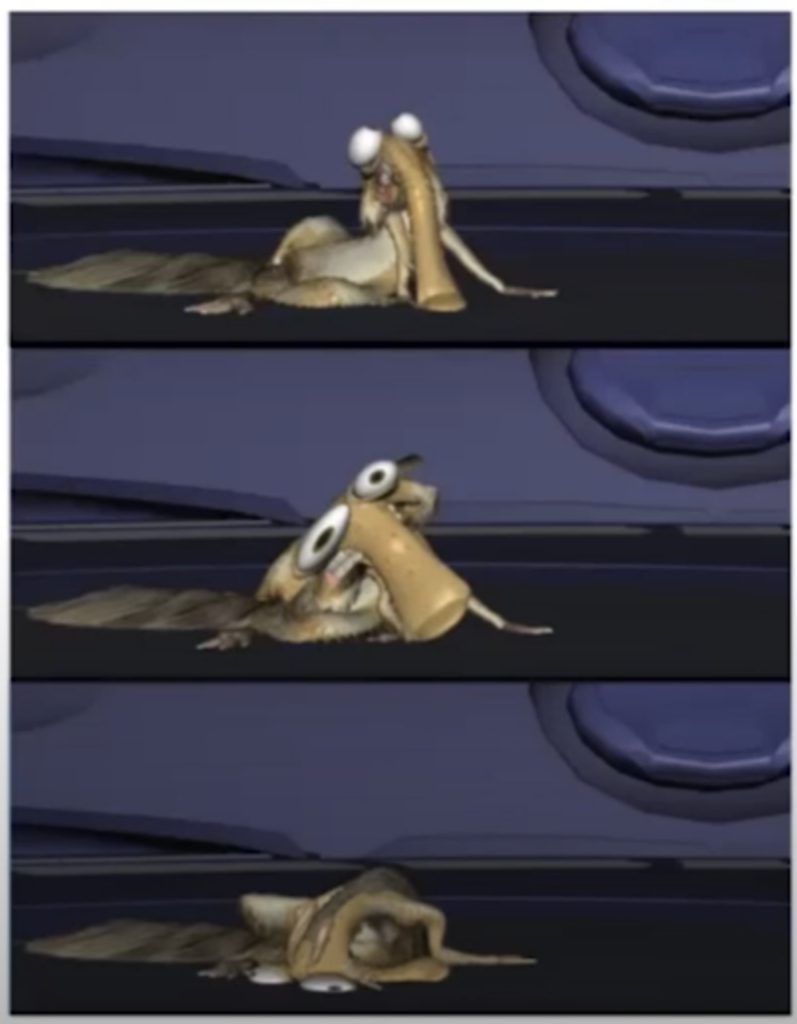
An example of a character lifting a heavy bowling ball – the action of lifting the ball upwards and back creates momentum in that same direction, causing the character to step backwards to compensate for the change in center of gravity.

Note the difference in poses. In the upper example, the character stands straight—if they tried to push a box, it wouldn’t appear heavy/work properly because the center of gravity is straight with the body. In the lower example, the character’s pose allows for more force to be applied towards the box, indicating that it is heavy and requires more effort to be moved.
Gravity also plays a major role in how we perceive weight. Heavy objects fall faster and take longer to change direction. This principle can be applied through proper spacing—using arcs that accelerate as objects fall and decelerate as they rise or shift direction. Even spacing takes away from believability and realism, feeling robotic and stiff; instead, variation in timing and arcs gives the impression of mass and momentum.
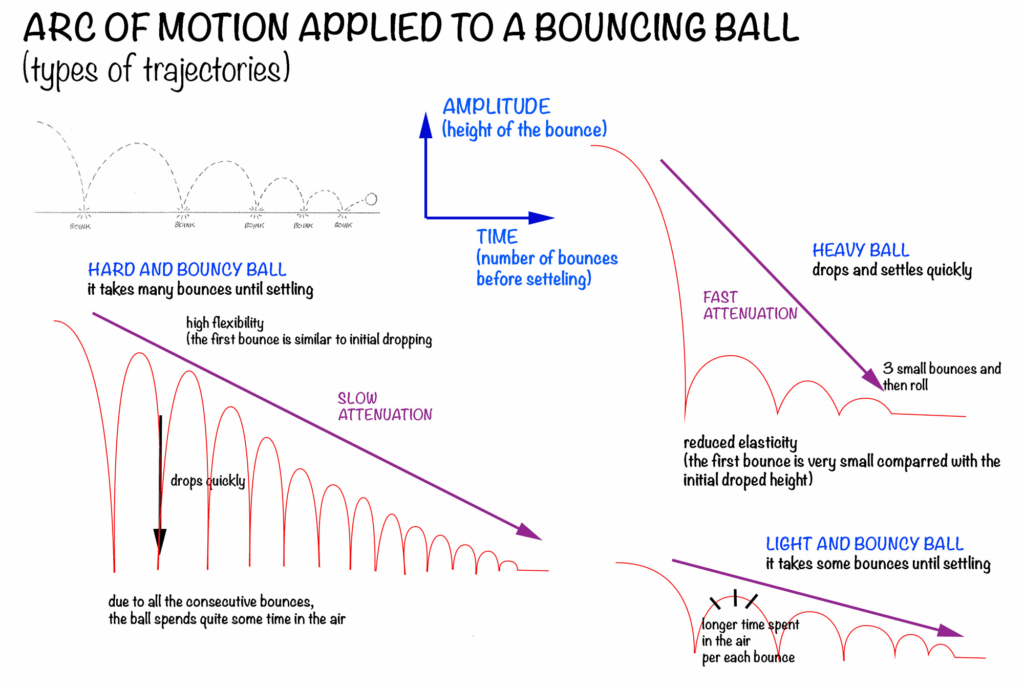
From cristinateachingart.com
Storytelling in animation goes beyond motion—it’s about intent and response. If a character tries something that doesn’t work, they should visibly readjust and try harder. This adds realism and emotional depth, creating a much more compelling shot. Whether it’s a simple lift or a complex push, mastering these principles of force and weight is essential to creating realistic animations that resonate with audiences.
Watch the full clip from an AnimSchool lecture here:
At AnimSchool, we teach students who want to make 3D characters move and act. Our instructors are professionals at film and game animation studios like Dreamworks, Pixar, Sony Pictures, Blizzard & Disney. Get LIVE feedback on your Animation from the pros. Learn more at https://animschool.edu/