Staging in animation is the process of breaking down a story into the most simple and basic beats in order to provide a foundation with which to further manipulate the scene into something more unique and entertaining. It is about setting the stage for your character’s actions, ensuring the camera is in the right place, and conveying the story in the simplest, most effective way possible. In this clip from a live AnimSchool lecture, instructor Tyler Phillips breaks down an alien abduction scene from former student Jonah Sidhom.
In Sidhom’s example, the character begins sleeping and wakes up to an alien, reacts, and runs away, ultimately being sucked out into space. This sequence is a clear example of staging that conveys an entire story using only six simple beats. These beats guide the viewer through the character’s emotional and physical journey, from initial confusion to their final fate.

Staging can start with basic visual storytelling elements: simple poses and camera placements. As in the alien scenario, a character might move across the scene, push a button, and face multiple challenges. Each of these actions becomes a beat—an individual piece of the animation that, together, creates the flow of the narrative.
The key to effective staging is to capture not just the actions but the emotions behind those actions. Adding “thinking beats”—moments when the character pauses to react or assess the situation—creates depth and engagement. For example, a character might look at an alien, then pause, registering the danger, and only then react with a frantic escape.

Additionally, creating more granular acting beats can add texture and realism. In one instance, when the character slams against a wall, the small moment of bounce and holding that pose for just a couple of frames enhances the readability of the action. This small pause gives the viewer enough time to process the action before moving to the next step, ensuring the sequence is clear and believable.
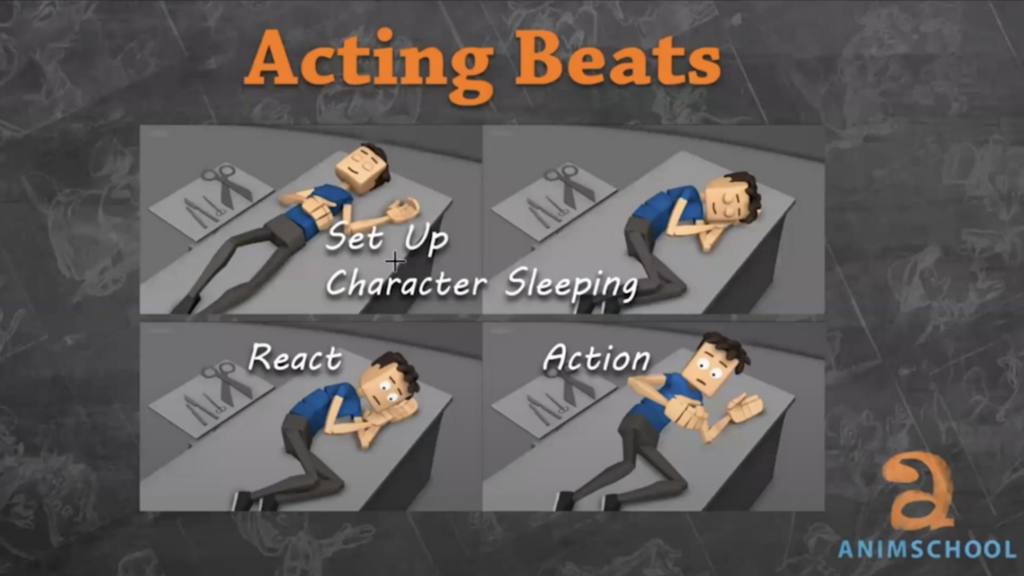
One of the most important aspects of animation is variety—using quick, medium, and slow beats. A variety of pacing helps keep the audience engaged and ensures the shot feels dynamic. These contrasting rhythms add richness to the animation, making it feel more alive and less mechanical.
In professional animation, the focus is on bringing characters to life. They must be believable in their thoughts and actions, reacting to their environment. An animator’s job is to think about these moments of reaction and transition, creating a character that feels genuinely alive. Though seemingly small and perhaps even insignificant, intentionally placed acting beats are what ultimately make characters feel real and relatable.
Watch the full clip from an AnimSchool lecture here:
At AnimSchool, we teach students who want to make 3D characters move and act. Our instructors are professionals at film and game animation studios like Dreamworks, Pixar, Sony Pictures, Blizzard & Disney. Get LIVE feedback on your Animation from the pros. Learn more at https://animschool.edu/



