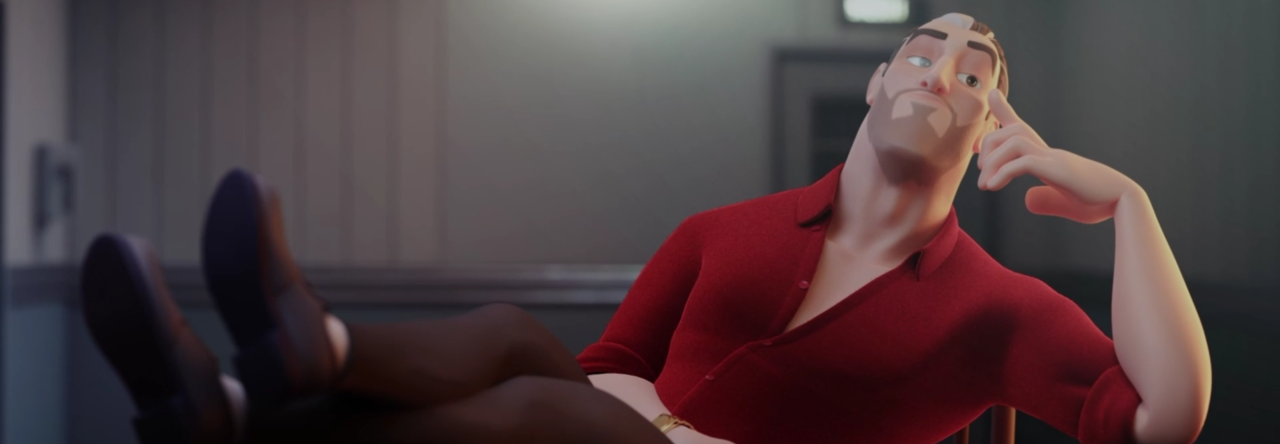
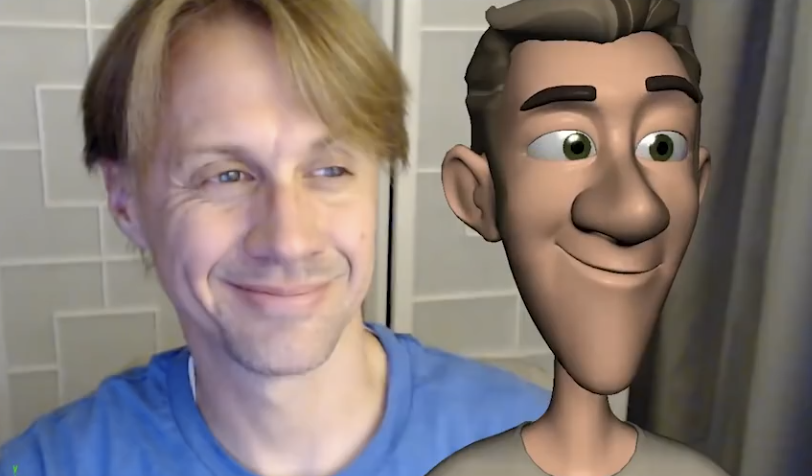
One of the biggest challenges in designing facial expressions for animation lies in deciding how realistic or exaggerated the design should be. Interpreting and adapting real-life references plays an important role, but it’s also essential to understand when to push the boundaries of realism to better convey emotion and expression. In this clip from a live AnimSchool lecture, instructor Hans Dastrup demonstrates using a reference image to create a more stylized and appealing pose for the face.
One key to effective facial animation is understanding the balance between mimicking real-life expressions and adjusting them to suit the character and animation style. Avoid directly copying facial expressions from reference material without considering the unique needs of the character, as replicating a facial expression exactly as it appears in real life does not always translate well in animation. Mimicking expressions can often result in awkward or less appealing designs, especially if the goal is to achieve clarity and emotional impact.

Matching the reference exactly.
To create a more visually pleasing expression, subtle changes, like simplifying, are often necessary. For instance, in the process of creating a smile, adjusting the mouth shape and adding slight asymmetry can go a long way, as real human faces are inherently asymmetrical and can help maintain a more natural look. A smile in real life might have one side slightly higher than the other, and exaggerating this asymmetry can enhance the character’s expression.
When working with the eyes, it’s important to consider the character’s anatomy. In animation, characters often have larger eyes with exaggerated white areas, which can make them appear more expressive. However, it’s crucial to avoid pushing this too far, as extreme eye shapes can lead to unnatural or unsettling appearances. By adjusting the eye shape slightly, such as making the lower eyelid flatter, a more balanced and appealing look is created without overdoing the exaggeration.

Adjusted eye and mouth shapes to incorporate asymmetry.
Another important consideration is the character’s overall design. For instance, in a happy character, a more graphic and simplified mouth shape may work better than trying to replicate a realistic smile. Pushing the design in this way helps to exaggerate the emotion and adds visual clarity, making it more readable to the audience. The expression doesn’t have to be entirely unrealistic must be entirely unrealistic—it’s about finding the right level of push to enhance the emotion without distorting it beyond recognition.

Pushing the final expression.
While it’s important to consider real-life references, animation often requires tweaking those references to fit the style and emotional needs of the character. By simplifying, adding asymmetry, and adjusting features like the eyes and mouth, animators can create more engaging and believable facial expressions that convey the intended emotion. Ultimately, the goal is to find the balance between realism and stylization to craft a performance that resonates with the audience.
Watch the full clip from an AnimSchool lecture here:
At AnimSchool, we teach students who want to make 3D characters move and act. Our instructors are professionals at film and game animation studios like Dreamworks, Pixar, Sony Pictures, Blizzard & Disney. Get LIVE feedback on your Animation from the pros. Learn more at https://animschool.edu/